What is a Motherboard?
The motherboard is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in a computer. It acts as the central hub that connects all components—like the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and input/output devices—so they can communicate and function together.
The motherboard holds and allows communication between the electronic components of a system. All the other components are located on or plugged into it (the CPU, the RAM, the graphics card etc.)
The Motherboard is the heart and biggest circuit board of the computer.
The computer’s main circuit board that contains different components that are soldered and non-removable, as well as the removable ones with slots or sockets.
The Houses
Motherboard Connect everything together & It is the part of the computer that houses the CPU chips, and the ROM and RAM chips, etc.
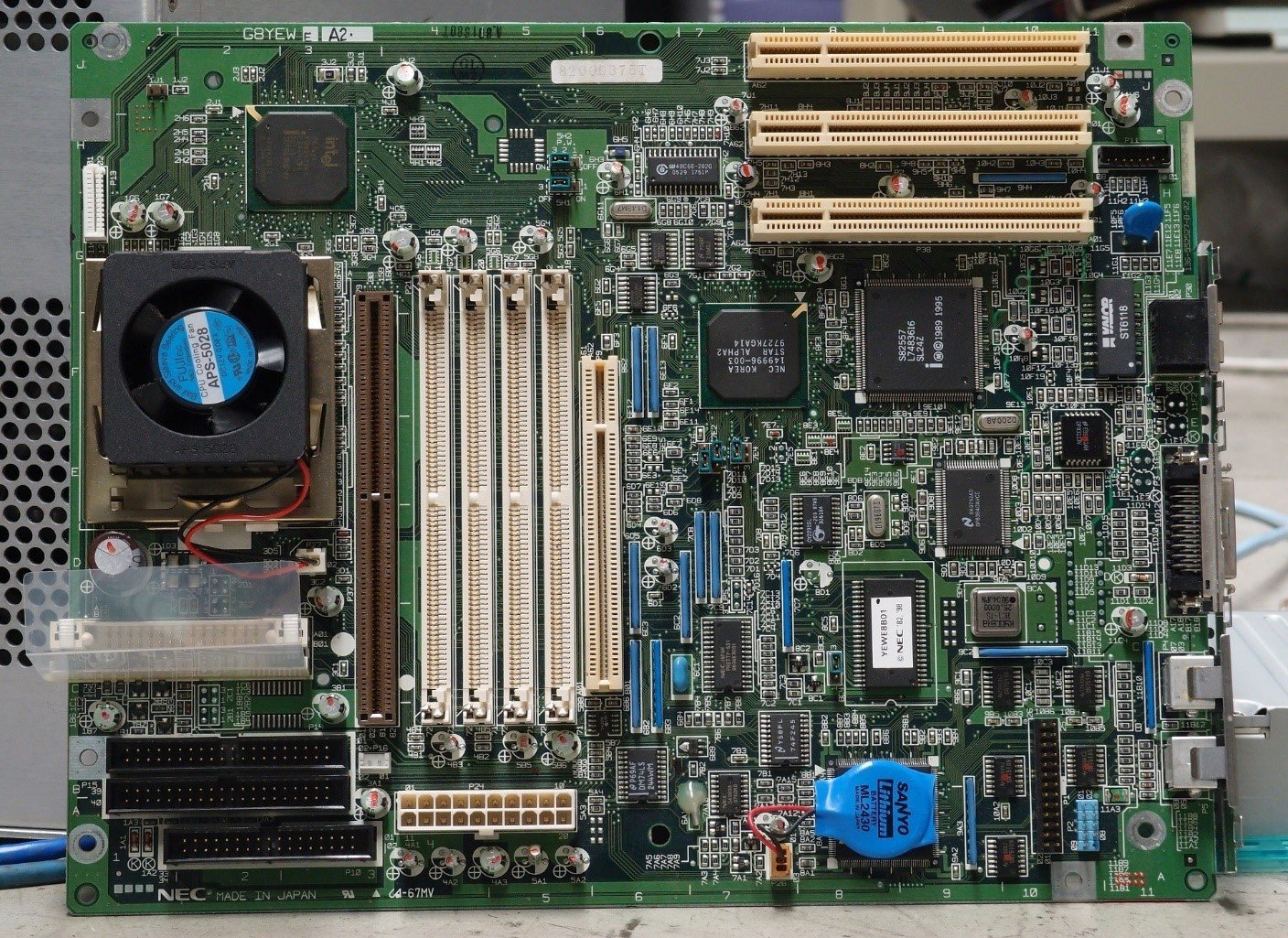
1. The Connections
All other components and Peripheral devices are connected to the motherboard, and thus, rightfully called the motherboard.
2. Functions of the Motherboard:
- Houses the CPU (Central Processing Unit) – the brain of the computer.
- Holds RAM slots for system memory.
- Connects storage devices (HDDs, SSDs).
- Provides power distribution from the PSU to components.
- Enables communication between components via buses and chipsets.
- Contains BIOS/UEFI firmware for hardware initialization.
- Offers expansion slots (PCIe) for graphics cards, sound cards, etc.
- Provides ports for USB, audio, LAN, video output, etc.
3. Types of Motherboards (Based on Use):
Typical form factors include ATX (most common), microATX, ITX, and BTX.
- Desktop Motherboards – For general computing, gaming, or workstations.
- Laptop Motherboards – Customized to fit specific laptop models.
- Server Motherboards – Designed for high stability, more CPU sockets, and memory channels.
- Embedded Motherboards – Used in industrial and IoT devices.
4. Common Motherboard Sizes (Form Factors):
- ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended) – Standard size; most common in desktops.
- MicroATX (mATX) – Smaller than ATX; fewer slots.
- Mini-ITX – Very compact; used in small-form-factor PCs.
5. How It Works:
When you power on a computer:
- The BIOS/UEFI on the motherboard initializes the hardware.
- It checks and detects devices (CPU, RAM, drives).
- The CPU, RAM, and GPU work together using the chipset to process data.
- Data travels through circuits and buses (like PCIe, SATA, USB) on the motherboard.


